Vaccination is of vital importance to protect us against the virus and, in the current situation, to improve the pandemic situation. They help us to generate immunity against different diseases.
Vaccines work by introducing, in different ways, the element against which we want our body to generate immunity and, thus, when we come into contact with that element, the body is more prepared to fight it.
The benefits of vaccines are infinitely superior to the problems they may cause, so it is very important to get vaccinated to help the body generate protection.
To combat the coronavirus, different vaccines have been developed that work by different mechanisms. Do you know the differences between the different SARS-CoV-2 vaccines currently on the market?
Differences between the different vaccines available on the market
There are currently two main types of licensed vaccines, both of which are safe and effective:
- mRNA vaccines: these vaccines contain the genetic material of the virus that causes COVID-19. This genetic material promotes our cells to generate a protein from this genetic material (which is not harmful) and is exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. Once this protein is created, copies of it are made, which the body recognizes as foreign and sets in motion the immune machinery to fight them by generating T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes. These lymphocytes will help us to fight the virus if we are exposed to it in the future.
This is the case of vaccines such as Pfizer-BioNTech’s Moderna or, the next one to be launched on the market, CureVac. - Viral vector vaccines: A viral vector is like a “Trojan horse” that carries the fragment of the virus against which we want to generate immunity. In this type of vaccine, a virus different from the COVID-19 virus is inoculated and its genetic material is modified to include genetic material from SARS-CoV-2. Once the genetic material of the virus is released, our body generates the virus protein and its corresponding copies. These copies set in motion the necessary immune machinery, generating T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, which will help us fight the disease.
In this group are the Janssen or Astrazeneca vaccines.
In neither of these cases the SARS-CoV-2 virus is inoculated in an active state, so this type of vaccine cannot produce the disease. The body, upon detecting an external substance and triggering the immune system, may react and, therefore, possible side effects may occur.
Therefore, the differences between the various vaccines available are based primarily on the mechanism of entry of the genetic material into the body.
How do vaccines work? Can their efficacy be measured?
In conclusion, as a summary of the process in a simple and summarized way, the following steps would occur:
- The genetic material of the virus is introduced by different mechanisms.
- Our body generates a protein from the inoculated genetic material, which is specific to the virus, the S protein.
- Multiple copies of this protein are generated.
- Our body sets in motion the immune machinery against the protein, generating the lymphocytes mentioned above.
- The B lymphocytes, in turn, generate antibodies against this protein. These antibodies will help us to be protected against the virus in case of contact with it.
When a coronavirus infection occurs, the body generates antibodies of all types against the different proteins found in the structure of the virus (N protein, M protein, E protein and S protein). However, with vaccines, only antibodies against protein S are generated.
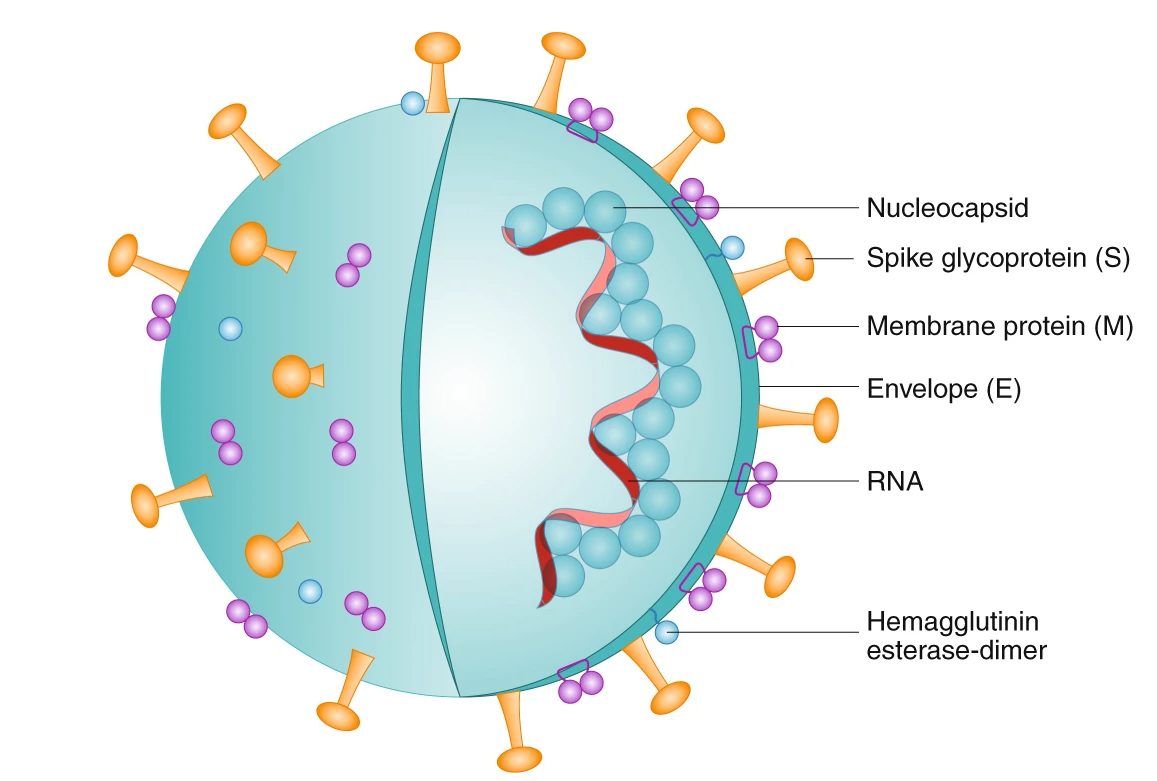
Source: Florindo, H.F., Kleiner, R., Vaskovich-Koubi, D. et al. Immune-mediated approaches against COVID-19. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 630–645 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0732-3
In this regard, there are numerous serological tests on the market that allow the detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, but most of them detect the N protein of the virus, so they would not be useful to evaluate the efficacy of vaccines.
However, at Biolan Health we have developed a serological test that can detect neutralizing antibodies, which are those antibodies directed against the receptor binding region RBD of protein S. This region functions as a “key” for the virus to enter the human cell. Therefore, by detecting specific antibodies against the protein generated by vaccines, our test is an ideal tool for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Did you like this post? You can subscribe to our newsletter to receive blog updates and the latest news!


